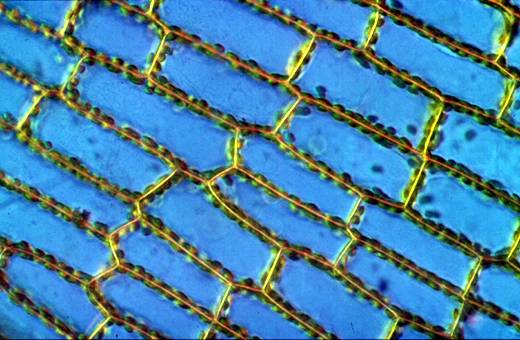
Membrane (Latin membrana,"parchment"), in biology,
any thin layer of connective tissue coating individual
cells and organs of the body, or lining the joints and
the ducts and tracts that open to the exterior of the
body. The membrane surrounding single-celled animals
and plants and individual cells in multicellular organisms
is important in the nutritive, respiratory, and excretory
processes of these cells. Such cell membranes are
semipermeable; that is, they allow the passage of small
molecules, such as those of sugars and salts, but not
large molecules, such as those of proteins. Structures
inside cells, such as the nucleus, may also have
|